Table of Contents
If websites are doing well on Google and showing up in the top 10 results, they’re definitely doing something right! Taking a closer look at them can help you climb to the top spots too.
While you can use tools such as Ahrefs and Semrush for SERP analysis, their free versions have limitations. To address this, I’ve developed a free SERP Analyser in google sheets, offering you a free and comprehensive tool for conducting a thorough SERP analysis.
In this post, I’ll guide you through the fundamentals of SERP analysis, provide setup instructions for the google sheet, and help you grasp how to integrate the SERP analysis process into your marketing strategy.
What is SERP analysis?
SERP Analysis is essentially analysing the quality of the pages that show up at the top of a search engine results page. This helps you figure out if putting in the effort to rank for a specific keyword is worth it or if there are better opportunities to focus on.
SERP analysis is an essential part of the content marketing process and should be performed along with keyword research.
About the free SERP analyser (using Google Sheets)
I created this Google Sheet template primarily for individuals operating on a tight marketing budget, unable to invest in SEO software. While paid subscriptions to tools like Ahrefs and Semrush offer more extensive analysis, I hope this Google Sheet template serves as a valuable starting point for marketers in their early endeavours. 😁
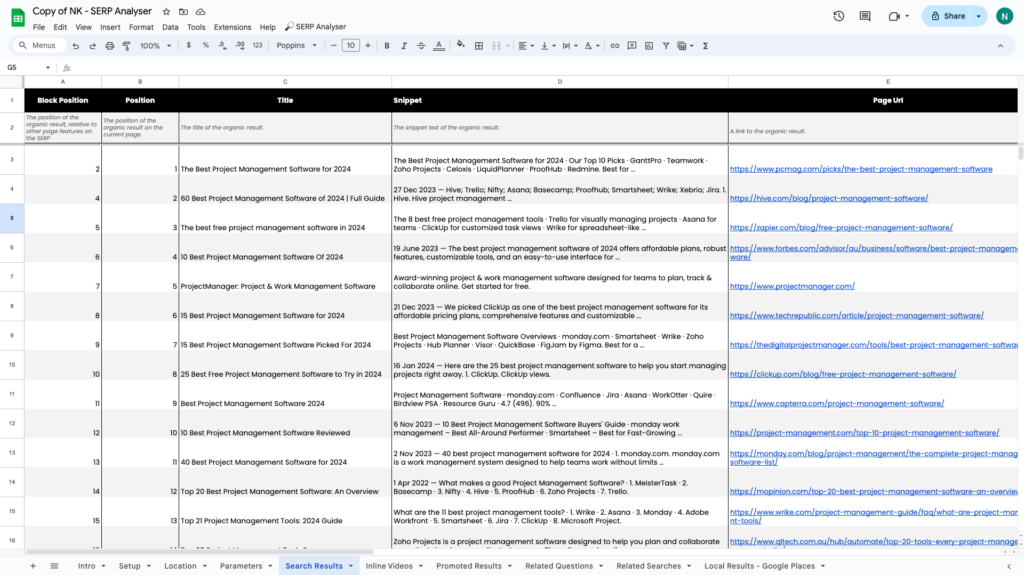
With this SERP analyser template, you can analyse the following:
- Organic Search Results
- Sponsored Search Results
- Related Searches
- Related Questions
- Local Results
With this Google Sheet template, you can access real-time, location-specific Google SERP data.
Hover over the black dots in the image below to see more details:
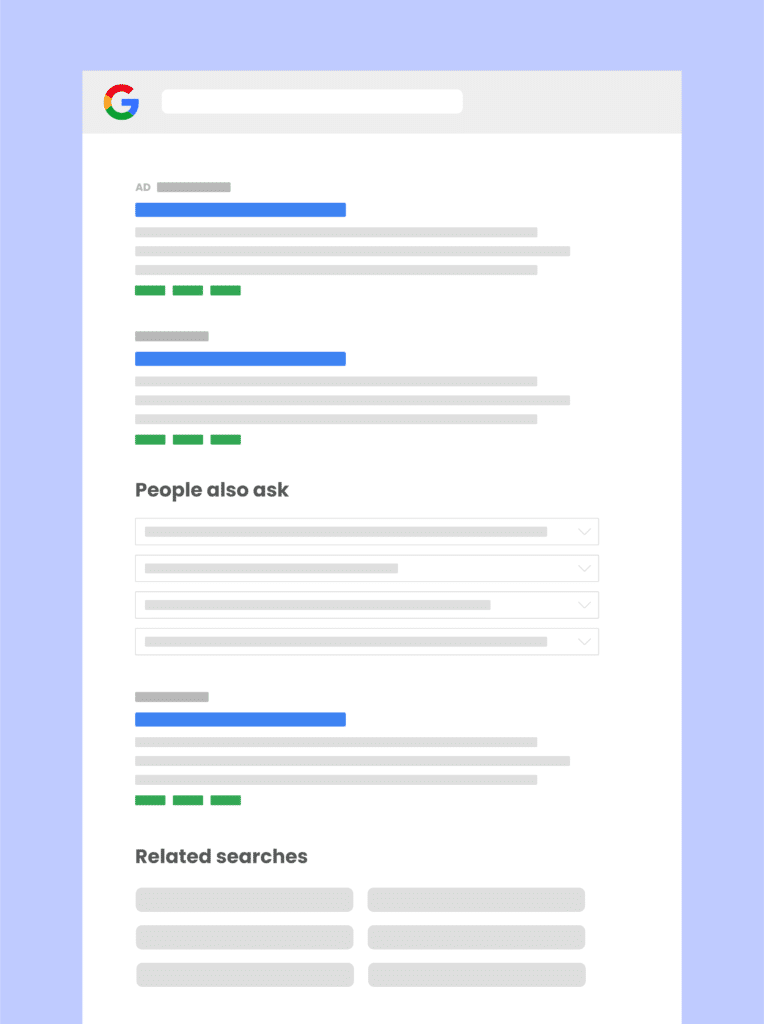
Sponsored Posts
Examine the data for all sponsored listings for any query.
Organic Results
Analyse the real-time organic results for any query, in any location and in any language. Additionally, retrieve URL details such as Page Authority, Domain Authority, and backlinks.
Related Questions
Get a list of all related questions - typically under the People also ask category. People Also Ask (PAA) is a Google SERP feature that provides users with related questions and answers to their original search query.
Related Searches
The related searches section is typically found at the bottom of the first search engine results page (SERP). It provides users with a list of search queries similar to the original query. They are also known as "people also search for," "people search next," and "refine this search".
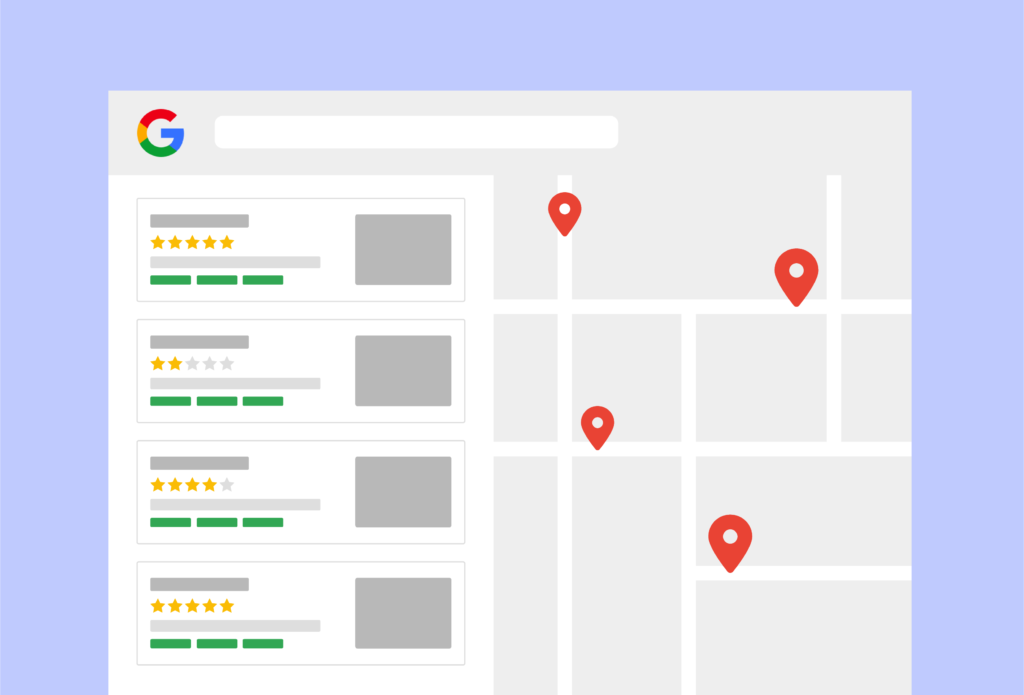
Local Results
Google local results appear when someone searches for a business in a specific geographic area.
Advantages & Limitations
Let’s explore the advantages and limitations of using this SERP Analyser google sheet template:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| 1. Free of Cost | 1. Provides SERP feature results in a separate sheet. |
| 2. Higher usage limits compared to free versions of tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, Mangools etc. | 2. Doesn’t provide information on SERP features, such as, knowledge graph, video carousels, top stories etc. |
| 3. Provides location-specific data | 3. Might lead to script timeout issues for large volumes of data. |
| 4. Provides real-time SERP data | |
| 5. Provides link data for search results (PA, DA, backlinks etc) |
SERP analyser setup
This sheet uses Scale SERP and Moz APIs to run. You’ll need to register on each of these websites and obtain API keys from them.
Lets have a look on how you can get these:
Scale SERP API
Scale SERP provides a free, real-time Google Search Results API. With the free plan, you get 125 free searches a month.
To get the API key, go to the Scale SERP website and sign up for the free tier plan.
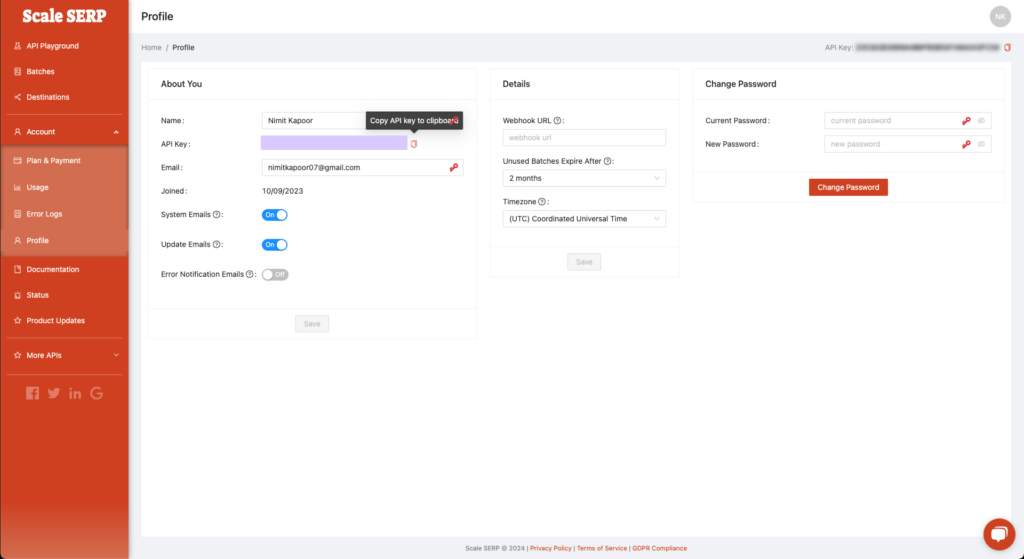
Once you’ve signed up, you’ll find your API key in the profile section of the dashboard.
Moz Pro API
First, you need to register and create an account on Moz. Once you’ve registered and activated your account, go to the Moz API pricing page and click on the Try it free button. You will have to enter your billing address and card details but don’t worry, you won’t be charged anything for this tool (provided you stay within the usage limits).
Moz is quite generous and allows up to 2500 rows per month.
To make it easy for all of you to track your usage of both APIs, I’ve also made a section in the google sheet where you can retrieve usage data for both these tools without ever having to leave the google sheet.
Once you’ve put in your credit card details, you can find your Access ID and Secret Key in the Moz API dashboard.
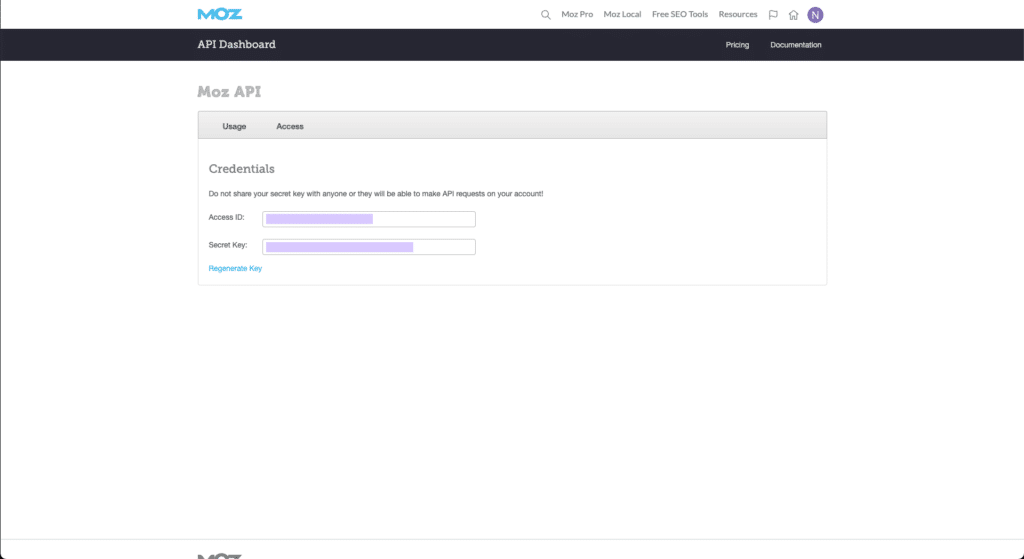
Google Sheet
Now it’s time to copy the google sheet template and start with the SERP analysis. To setup the google sheet, follow the steps below:
1. Make a copy
Open the google sheet template and click on Make a copy.
2. Input the keys
Paste the Scale SERP API Key and Moz’s Access ID and secret key in the relevant locations in the setup sheet.
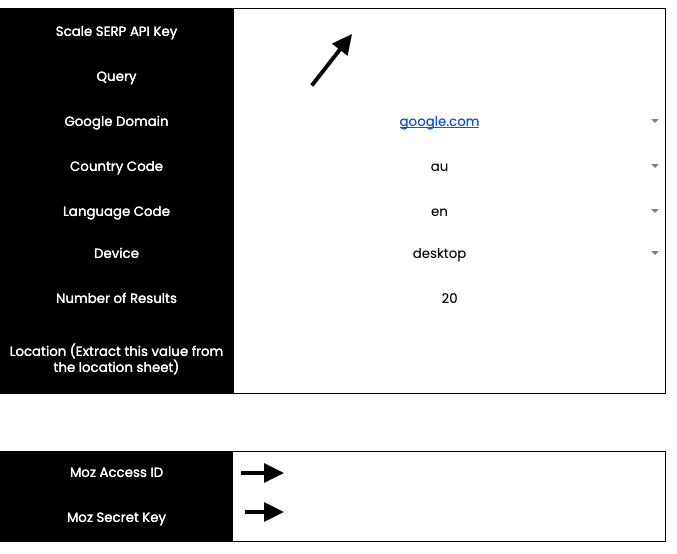
3. Set the search parameters
You can now select the google domain, country code, language code, device, no. of results and location.
For Google domain, country code and language code, I’ve created a sheet named parameters that’ll help you match the domain, country code and language easily. For example, if I wanted to conduct a search for Australia, I can put the domain as: google.com.au, the country code as: au and the language code as: en.
💡 It’s not always necessary that the google domain and language code matches every time. For instance, if I wanted to do a SERP analysis for India but I want English search results only – my Google domain will be google.co.in but the language code will be en.
The location section is used for localised results, if you want to conduct Google searches from a specific location, for example, a city or county. This I’ll cover in the local results section below. For now, let’s leave this field blank.
Now you’re ready to start analysing SERP results with this google sheet.
How to conduct SERP analysis?
Every individual tends to have their own unique methods for analysing SERP results. I’ll share my approach but if you have a different take, I encourage you to share it by putting it in the comment section below.
So this is what I do:
1. Analyse search intent
The first thing that I do is analyse the search intent and content types for a specific keyword. Before we show see how to analyse this in the google sheet template, let me explain you what I mean by search intent.
Search intent is basically figuring out what people are really after when they type stuff into a search engine. Here are four different types of search intent:
- Informational: When someone’s on the hunt for information, like “how to fix a leaky faucet” or “why do cats purr.”
- Navigational: Ever just want to get somewhere online? That’s navigational intent. Type in “YouTube” or “Twitter login,” and you’re on a direct route.
- Transactional: Time to take out the wallet. This is when people are ready to buy, like searching for “best deals on Air Jordans”.
- Commercial: This is the window-shopping phase. People are digging into reviews, comparisons, trying to decide before making a move. Think “top-rated smartphones 2024.”
And by content types, I mean whether the search result is a blog post, product page, category page, video, listicle etc.
Let’s say I want to analyse the SERP results for the keyword “project management software“. I can type in the keyword next to the query in the setup sheet, set my google domain, country and language codes – and then from the SERP analyser menu option, click on Run SERP Analyser.
The first time you run the google sheet app script, you might have to give authorisation and click on Run SERP Analyser again. See the video below:
On analysing the search results, we can see that the query “project management software” is informational and it’s quite evident that most of the top organic search results are blog posts.
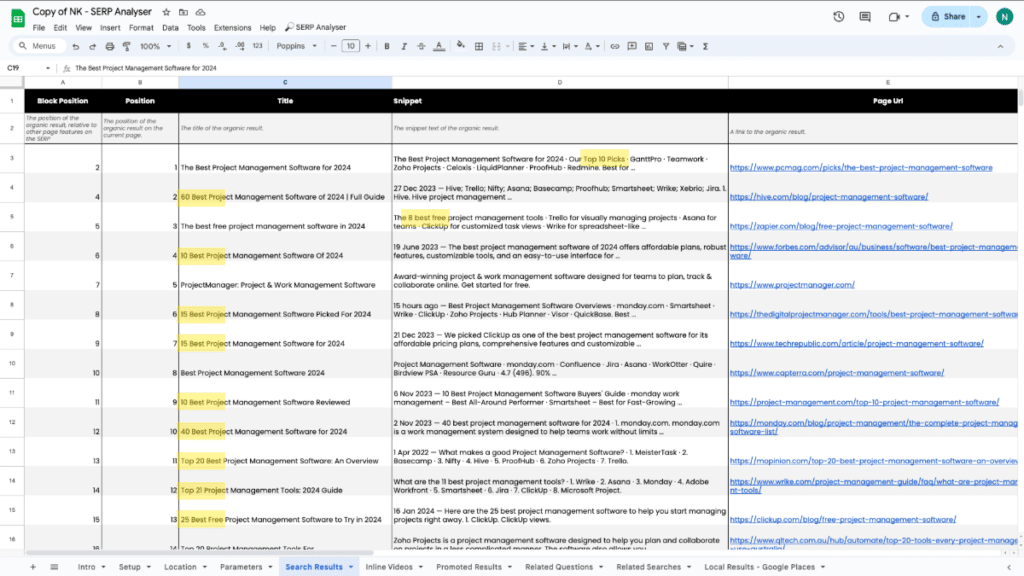
With this query, people expect to find more information on the various project management software and want to read a post by someone who might have tried different options before they actually purchase.
With the help of this tool, now I know what type of content I need to create to rank for this query.
But just analysing the search intent and type of content is not enough. I need to know how easy it is to rank for this keyword. For this, I need to analyse the competition.
2. Analyse the competition
When diving into competition analysis, I follow a two-step process. Initially, I check if I’m currently ranking for the keyword and then compare my rankings with those of my competitors.
To easily identify your position in comparison to competitors, you can use the highlight competitors function. First enter your domain and your competitors’ domains in the setup sheet. In the same project management software example, lets say I’m working for atlassian and my competitors are monday, project manager and asana.
This is what my setup sheet would look like (put root domains, without https, www or trailing slashes):
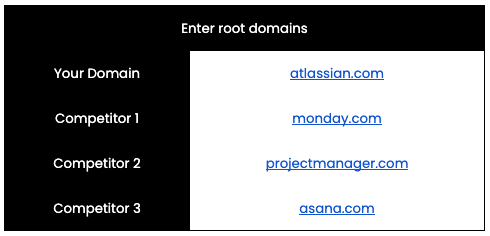
Once I’ve put all the domains, just select the Highlight Competitors option in the SERP Analyser 🔎 menu and it’ll highlight your domain in green and the competing domains in red.
This helps you gauge how your website stacks up against the competition.
After completing the initial steps, I proceed to conduct a link analysis for all the top domains on the SERP for the specified query. This step yields crucial information about competitors’ websites, including Domain Authority (DA), Page Authority (PA), and their backlink profile. This analysis assists me in determining whether pursuing this keyword makes sense or if redirecting my efforts elsewhere would be more beneficial.
To do this, all you have to do click on Get Moz Link Data in the SERP Analyser menu option.
💡 This step might take a while to complete and can also timeout if you are working with a lot of SERP results. But don’t worry, if the script times out, just run it again and it’ll start from where it left off.
💡 You might get an error notification once all the links are analysed. You can just dismiss that.
Let’s analyse the results:
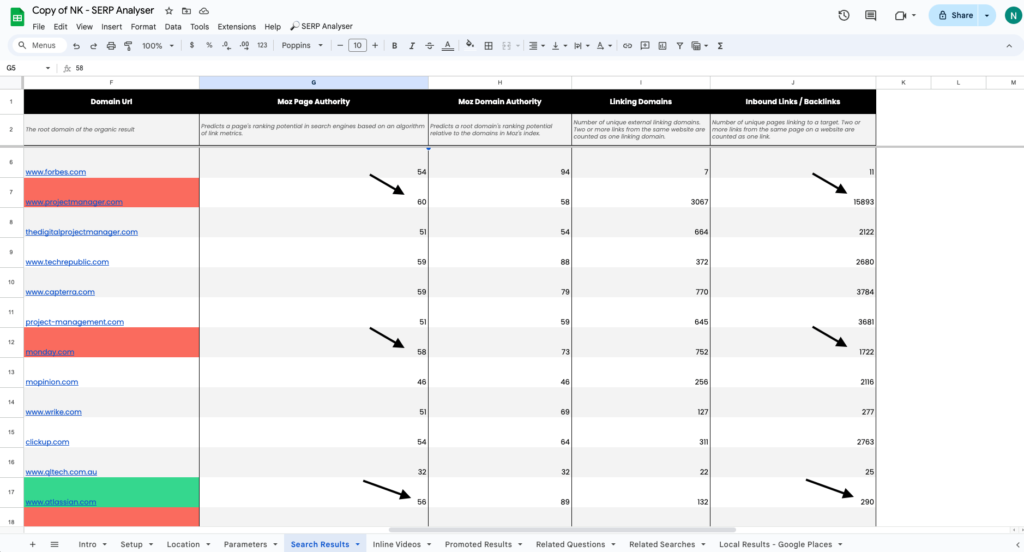
You can see the difference between the backlinks or page authority between the competing domains. It’s clear that to compete with domains like monday.com and projectmanager.com for the query “project management software”, Atlassian will have to get some more backlinks from different sources.
3. Identify new content opportunities
Looking at related questions (aka People also ask) and related searches can be a great way to identify new content opportunities.
To get the related questions and related searches, you just have to Run the SERP analyser, it fills in the related searches and related questions sheets as well along with the search results sheet.
Let’s look at the SERP results for the keyword “healthy smoothie recipes“.
Related Questions
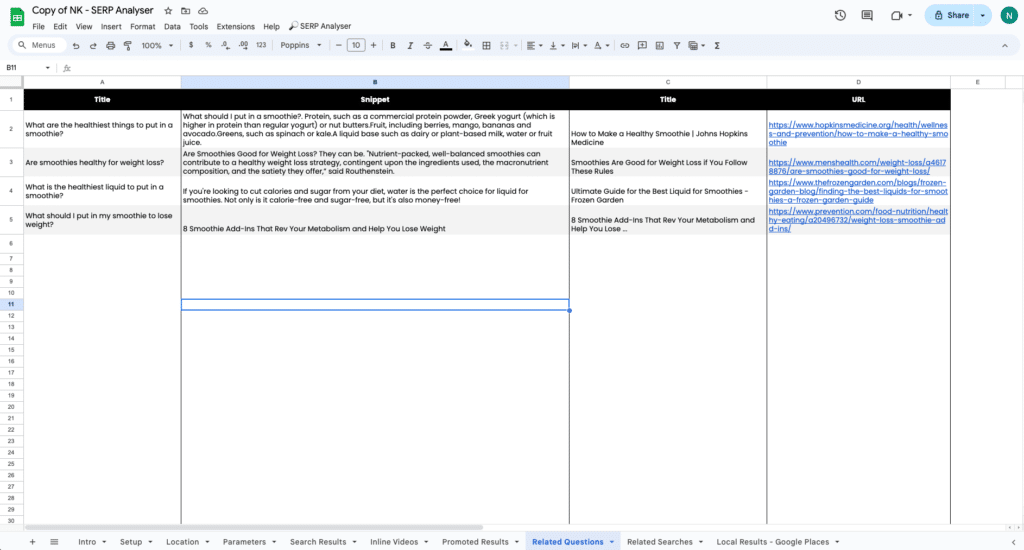
Lets see the first related question that people ask: “What are the healthiest things to put in a smoothie?”
I can either incorporate this in my existing content or create a blog post and video on the topic “Top 10 healthy ingredients for a nutrient-packed smoothie” to cover it in more details.
Related Searches
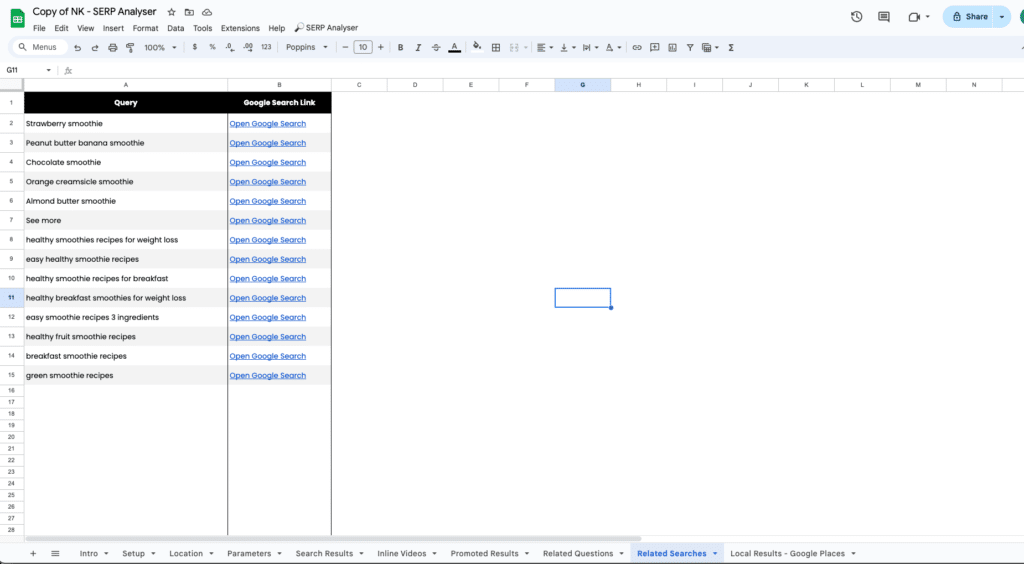
Looking at the related searches, I have a lot of new content ideas that I can work on. I know people also search for different smoothie recipes, specifically: strawberry, peanut butter banana, chocolate, orange creamsicle and almond butter. So it might be worth putting recipes for these smoothies on my site (Bonus – add recipe schema to generate rich results for these queries).
4. Analysing SERP results for local businesses
For analysing local results, you will want to narrow down to specific cities or locations. For this, I’ve integrated Scale SERP’s location API as well that will help you get accurate locations that you can use while generating local SERP results.
To do this, first open the locations sheet and enter the area that you want to use as your location. Once you’re done with that, click on Get locations option from the SERP Analyser menu. This will give you a list of Scale SERP supported Google search locations.
Let’s say I want to conduct a local place search for cafes in Sydney, Australia. I’ll run the Get locations function and get different locations (suburbs) that I can use to narrow down my Google search to that specific location. Have a look: 👀
To get local results, copy the location full name and paste it in the location section in the setup sheet, like this:
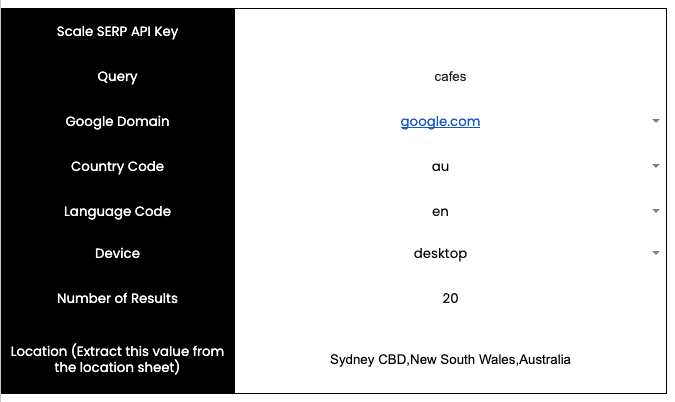
Then click on the get Local Google Places Result from the SERP analyser menu.
5. Checking Usage Data
So that you don’t end up exceeding the usage limits of Scale SERP and Moz while using this free SERP analysis google sheet template, I’ve created a function that you can run to check your API usage.
To do this, just click on the Update Usage Details and it’ll populate the setup sheet.
Final thoughts
Conducting a SERP analysis may sound daunting at first, but I hope this free SERP Analyser makes it easy for you.
I’m planning to tweak and upgrade it as we go. Any thoughts on what you’d love to see in the tool? Pop them in the comments below, and let’s make it even more awesome! 💪🏻

3 Responses
I I use this tool quite regularly, it’s just perfect, thank you very much. I can scrape the SERP efficiently, and access the PAA quickly.
However, as of this morning, the “SERP Analyser” button to launch the analysis is no longer present. Do you know how to fix this?
Hi Hugo,
Could you please go to Extensions -> App Script and confirm if the OnOpen() function is there? If it has accidentally gotten deleted, you’ll face this issue.
If it’s there, you can give me access to your sheet (if you’re ok with it) and I can have a look.
Hello Nimit, thanks a lot, it looks liked App Script was bugging only for a day. It worked after, without any changes. But once again thanks a lot for your answer, and as well, for your tool that I’m using frequently 🙂